9036. Dice combinations
Your task is to
count the number of ways to construct sum n
by throwing a dice one or more times. Each throw
produces an outcome between 1 and 6.
For example, if n = 3, there are 4 ways:
·
1 + 1 + 1
·
1 + 2
·
2 + 1
·
3
Input. One integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106).
Output. Print the number of ways modulo 109 + 7.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
3 |
4 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
Let f(n) be the number of ways one can get the
sum n. Let the number k (1 ≤ k ≤ 6) fell on the
last throw. Then all throws except the last one should get the number n – k, which can be
done in f(n – k) ways. Thus, we
have:
f(n) = f(n – 1) + f(n – 2) + f(n – 3) + f(n – 4) + f(n – 5) + f(n – 6)
The sum n = 1 can only be
obtained in one way, by rolling the dice once and getting 1 on it, so f(1) = 1.
The sum n = 2 can be obtained
in two ways: 1 + 1 and 2, so f(2) = 2.
Let n = 3. We can:
·
get 3 with one throw;
·
get 2 with the last throw and get 1
with the rest throws, which can be done in f(1) = 1 way;
·
get 1 with the last throw and get 2
with the remaining throws, which can be done in f(2) = 2 ways;
Thus f(3) = 1 + f(1) + f(2) = 1 + 1 + 2 = 4.
Similarly, for n ≤ 6 we have: f(n) = 1 + f(1)
+ f(2) + … + f(n – 1).
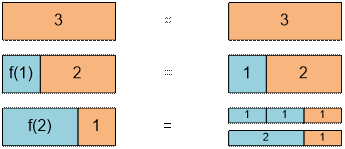
Consider our recurrence again:
f(n) = f(n – 1) + f(n – 2) + f(n – 3) + f(n – 4) + f(n – 5) + f(n – 6)
Write the
equation for f(n – 1):
f(n – 1) = f(n – 2) + f(n – 3) + f(n – 4) + f(n – 5) + f(n – 6) + f(n – 7)
From the last equation find the sum
f(n – 2) + f(n – 3) + f(n – 4) + f(n – 5) + f(n – 6) = f(n – 1) – f(n – 7)
and substitute it into the original recurrence:
f(n) = f(n – 1) + f(n – 1) – f(n – 7) = 2 * f(n – 1) – f(n – 7)
Compute the values of
the function for n ≤ 6:
f(1) = 1, f(2) = 2, f(3) = 4,
f(4) = 1 + f(1) + f(2) + f(3) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 4
= 8,
f(5) = 1 + f(1) + f(2) + f(3) + f(4) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 4
+ 8 = 16,
f(6) = 1 + f(1) + f(2) + f(3) + f(4) + f(5) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 4
+ 8 + 16 = 32
We got the equivalent
recurrence:
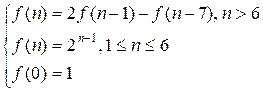
Example
Compute the values of the function f(n) for n ≤ 9.
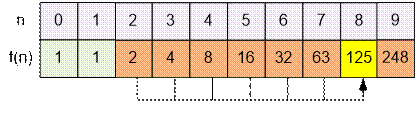
For example
f(8) = f(7) + f(6) + f(5) + f(4) + f(3) + f(2) = 125,
f(9) = 2 * f(8) – f(2) = 2
* 125 – 2 = 248
Algorithm realization
Declare the constants. Declare an array for computations.
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX
1000001
#define MOD
1000000007
long long dp[MAX];
The main part of the
program. Initializing values from dp[1] to dp[6].
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = dp[1] + 1;
dp[3] = dp[1] + dp[2] + 1;
dp[4] = dp[1] + dp[2] + dp[3] + 1;
dp[5] = dp[1] + dp[2] + dp[3] + dp[4] + 1;
dp[6] = dp[1] + dp[2] + dp[3] + dp[4] + dp[5] + 1;
Read the input value of n.
scanf("%d", &n);
Compute the values dp[7], …, dp[n].
for (i = 7; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] =
(dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + dp[i - 3] + dp[i - 4] + dp[i - 5] + dp[i - 6]) % MOD;
Print the answer.
printf("%lld\n",
dp[n]);
Java realization
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
static long dp[] = new long[1000001];
static long MOD = 1000000007;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[i] = 1 << (i - 1);
int n = con.nextInt();
for (int i = 7; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = (2 * dp[i - 1] - dp[i - 7] + MOD) % MOD;
System.out.println(dp[n]);
con.close();
}
}